Short Answer
|
|
|
Exhibit 9-3
Assign R, S configurations to each indicated
chirality center in the molecules below. 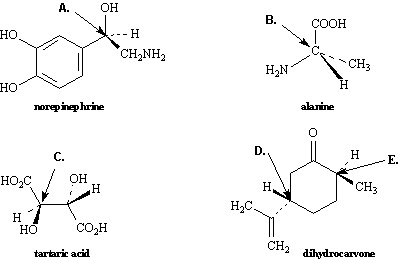
|
|
|
1.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (A) is
_____.
|
|
|
2.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (B) is
_____.
|
|
|
3.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (C) is
_____.
|
|
|
4.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (D) is
_____.
|
|
|
5.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. The configuration of this carbon atom (E) is
_____.
|
|
|
Exhibit 9-4
Consider the structure of streptimidone to answer the
following question(s). 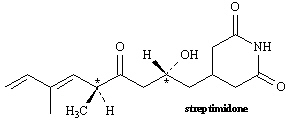
|
|
|
6.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-4. Assign R or S configuration to each
chirality center indicated in streptimidone.
|
|
|
7.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-4. Based on the number of chirality centers, how many
stereoisomers of streptimidone are possible?
|
|
|
8.
|
Refer to Exhibit 9-4. Will streptimidone have a meso stereoisomer?
Explain your answer.
|
|
|
Exhibit 9-5
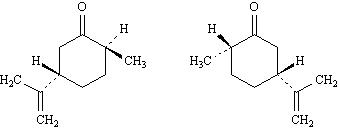
Label each pair of stereoisomers below as: | a. | enantiomers | | b. | diastereomers | | c. | identical | | |
Place the
letter of the correct answer in the blank to the left of the pair of stereoisomers.
|
|
|
9.
|
_____ 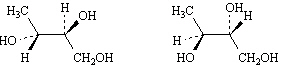
|
|
|
10.
|
_____ 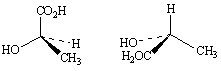
|
|
|
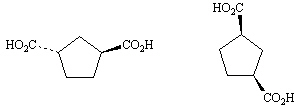
11.
|
_____ 
|
|
|
12.
|
_____ 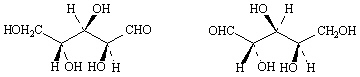
|
|
|
13.
|
_____ 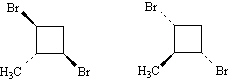
|
|
|
14.
|
_____ 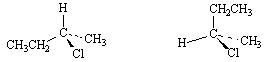
|
|
|
15.
|
_____ 
|
|
|
Exhibit 10-1
Give the name for each of the following alkyl
halides.
|
|
|
16.
|
Name: 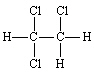
|
|
|
17.
|
Name:
CHI3
|
|
|
18.
|
Name: 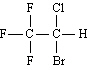 , Halothane
|
|
|
19.
|
Name:
CH2Cl2
|
|
|
Exhibit 10-4
Consider the reaction below to answer the following
question(s). 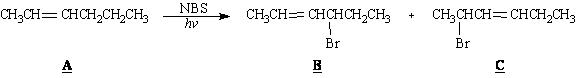
|
|
|
20.
|
Refer to Exhibit 10-4. Place asterisks(*) at all allylic positions in
compound A.
|
|
|
21.
|
Refer to Exhibit 10-4. Draw the resonance forms of the allylic radical
intermediate that accounts for the formation of B and C.
|
|
|
22.
|
Refer to Exhibit 10-4. D and E, below, are minor
products in this reaction. Explain why. 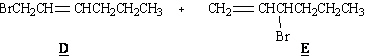
|
|
|
Exhibit 10-6
Provide structures for the reactants, intermediates, or
products, as indicated, in the following reactions. Draw the structures in the boxes provided.
|
|
|
23.
|
|
|
|
24.
|
|
|
|
25.
|
|
|
|
26.
|
|
|
|
27.
|
|
|
|
28.
|
|
|
|
29.
|
|
|
|
30.
|
|
|
|
Exhibit 10-5
Choose the best reagent or sequence of reagents
from the list provided below for carrying out the following transformations. Place the letter of your
response to the left of the reaction. | a. | PBr3 | d. | SOCl2, pyridine | | b. | HCl (gas), ether | e. | HBr (gas), ether | | c. | 1. | Mg,
ether | f. | 1. | Mg, ether | | | 2. | D2O | | 2. | NBS | | | | | | |
|
|
|
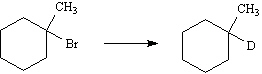
31.
|
_____ 
|
|
|
32.
|
_____ 
|
|
|
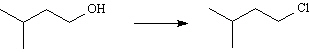
33.
|
_____ 
|
|
|
Exhibit 11-1
Circle your response in each set below.
|
|
|
34.
|
Circle the least reactive compound in an S N2
reaction. 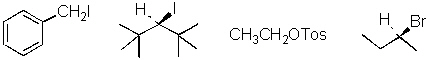
|
|
|
35.
|
Circle the best leaving group in an elimination reaction. 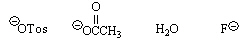
|
|
|
36.
|
Circle the best nucleophile in a substitution reaction at a primary
carbon. 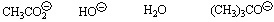
|
|
|
37.
|
Circle the least reactive compound in an S N1
reaction. 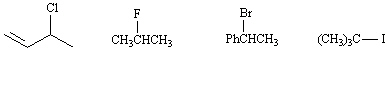
|
|
|
38.
|
Circle the best solvent for an S N2 reaction. 
|
|
|
Exhibit 11-3
Consider the pair of reactions below to answer the
following question(s). | a. | 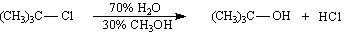 | | | | | | or | | | | | b. | 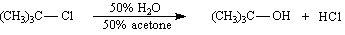 | | |
|
|
|
39.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-3. | a. | Which reaction above is faster? | | b. | Explain your answer to the
question in part a. | | |
|
|
|
40.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-3. The kinetics of these reactions are: | a. | second-order | | b. | first-order in
nucleophile | | c. | not
measurable | | d. | first-order in alkyl halide | | |
|
|
|
Exhibit 11-4
Consider the pair of reactions below to answer the
following question(s). | a. | 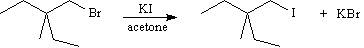 | | | | | | or | | | | | b. | 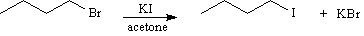 | | |
|
|
|
41.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-4. The alkyl bromide starting materials in these reactions
are classified as:
|
|
|
42.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-4. The solvent in these reactions is: | a. | nonpolar aprotic | | b. | polar aprotic | | c. | polar protic | | d. | nonpolar protic | | |
|
|
|
43.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-4. The nucleophile in these reactions is: | a. | K+ | | b. | alkyl group | | c. | Br- | | d. | I- | | |
|
|
|
44.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-4. Which reaction is faster?
|
|
|
45.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-4. The mechanism for these reactions is:
|
|
|
Exhibit 11-5
Consider the pair of reactions below to answer the
following question(s). | a. | 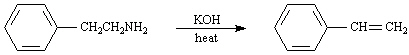 | | | | | | or | | | | | b. | 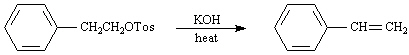 | | |
|
|
|
46.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-5. | a. | Which reaction above is faster? | | b. | Explain your answer to the
question in part a. | | |
|
|
|
47.
|
The original question has been combined with question #17 as part b. This
placeholder question is here to maintain the integrity of the numbering system between the printed
copy and ExamView. Therefore, it has been marked "do not use on test" in
ExamView's question information dialog. As a result, this placeholder question is
automatically prevented from being chosen as a test question.
|
|
|
48.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-5. Doubling the concentration of potassium hydroxide in
these reactions: | a. | causes the reaction mechanism to change | | b. | halves the rate of reaction | | c. | has no effect on the rate of
reaction | | d. | doubles
the rate of reaction | | |
|
|
|
49.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-5. The mechanism for these reactions is:
|
|
|
Exhibit 11-6
Consider the reaction below to answer the following
question(s). 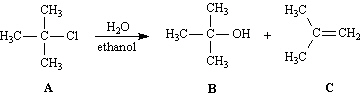
|
|
|
50.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-6. The substrate in the reaction is:
|
|
|
51.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-6. Compound B is the: | a. | SN2
product | | b. | SN1 product | | c. | E2 product | | d. | E1 product | | |
|
|
|
52.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-6. Compound C is the: | a. | SN2
product | | b. | SN1 product | | c. | E2 product | | d. | E1 product | | |
|
|
|
53.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-6. Write the complete reaction mechanism for the formation
of Compound C in this reaction.
|
|
|
Exhibit 11-8
Consider the reaction below to answer the following
question(s): 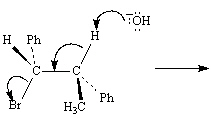
|
|
|
54.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-8. Write the product that results from the electron flow in
the reaction, clearly indicating any stereochemistry.
|
|
|
55.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-8. Draw a Newman projection of the reactive conformation of
the starting material.
|
|
|
56.
|
Refer to Exhibit 11-8. The mechanism of this reaction is:
|
|
|
Exhibit 11-10
Draw the structure of the major organic product(s) for
each of the following reactions. Indicate the stereochemistry for each reaction when
appropriate.
|
|
|
57.
|
|
|
|
58.
|
|
|
|
59.
|
|
|
|
60.
|
|
|
|
61.
|
|
|
|
62.
|
|
|
|
63.
|
|
|
|
64.
|
|
|
|
65.
|
|
|
|
66.
|
|
|
|
Exhibit 12-1
Select the most reasonable formula for the compounds with
the following mass spectral data.
|
|
|
67.
|
Refer to Exhibit 12-1. M + at m/z = 101 with a minor M+1
peak | a. | C5H6Cl | | b. | C5H12N2 | | c. | C6H15N | | d. | C9H12O | | |
|
|
|
68.
|
Refer to Exhibit 12-1. M + m/z = 136 and M + at
m/z = 138 of approximately equal intensity | a. | C6H13OCl | | b. | C4H9Br | | c. | C10H16 | | d. | C9H12O | | |
|
|
|
Exhibit 12-2
Use the data below to answer the following
question(s).
Loratidine is the active ingredient in the antihistamine Claritin®. Mass
spectral analysis of loratidine shows M+ at m/z = 382 and M+ at
m/z = 384 in an approximate ratio of 3:1 in intensity.
|
|
|
69.
|
Refer to Exhibit 12-2. The mass spectral data indicates that loratidine
contains: | a. | fluorine | | b. | chlorine | | c. | bromine | | d. | iodine | | |
|
|
|
70.
|
Refer to Exhibit 12-2. Loratidine is known to contain nitrogen. What is the
minimum number of nitrogens in loratidine?
|
|
|
Exhibit 12-5
Refer to the mass spectrum of 2-methylbutane shown below
to answer the following question(s). 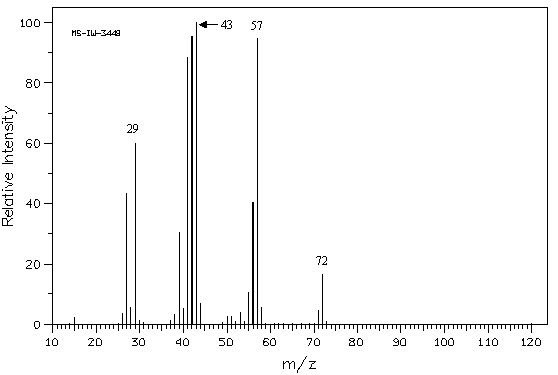 Spectrum obtained from: SDBSWeb:
http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS/
|
|
|
71.
|
Refer to Exhibit 12-5. What peak represents M+?
|
|
|
72.
|
Refer to Exhibit 12-5. What peak represents the base peak?
|
|
|
73.
|
Refer to Exhibit 12-5. Propose structures for fragment ions at m/z = 57,
43, and 29.
|
|
|
Exhibit 12-6
MATCH each of the following groups of bond-types to the
region of the infrared spectrum in which their absorptions occur. Place the letter of the region in
the blank to the left of the bond-type. | a. | 4000 to 2500 cm-1 | | b. | 2500 to 2000 cm-1 | | c. | 2000 to 1500 cm-1 | | d. | below 1500 cm-1 | | |
|
|
|
74.
|
_____ C-C, C-O, C-N, and C-X single-bond vibrations.
|
|
|
75.
|
_____ C=O, C=N, and C=C bond absorptions.
|
|
|
76.
|
_____ N-H, C-H, and O-H stretching and bending motions.
|
|
|
77.
|
_____ triple bond stretching vibrations.
|
|
|
Exhibit 12-7
At what approximate positions might the compounds below
show IR absorptions?
|
|
|
78.
|
|
|
|
79.
|
|
|
|
Exhibit 12-8
MATCH a structure from the list below to the following IR
spectra. Place the letter of the structure in the blank provided. 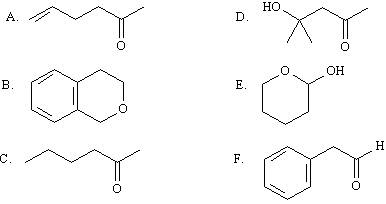
|
|
|
80.
|
_____ 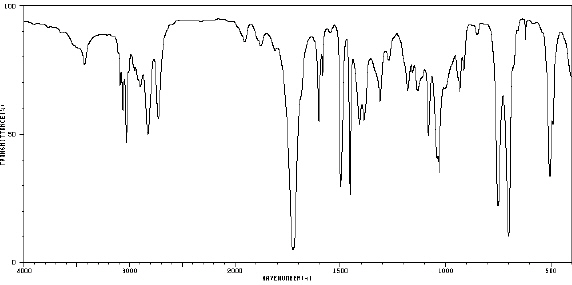 Spectrum obtained from: SDBSWeb:
http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS/
|
|
|
81.
|
_____ 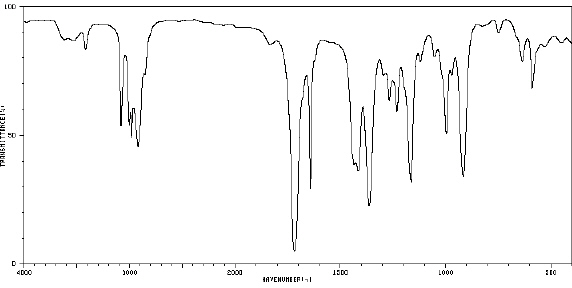 Spectrum obtained from: SDBSWeb:
http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS/
|
|
|
82.
|
_____ 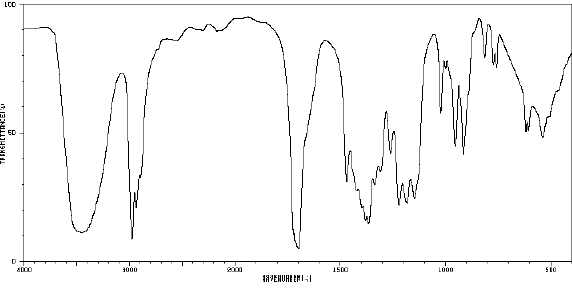 Spectrum obtained from: SDBSWeb:
http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS/
|
|
|
83.
|
Which structure of molecular formula C 4H 8Cl 2
fits both the 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra shown below? 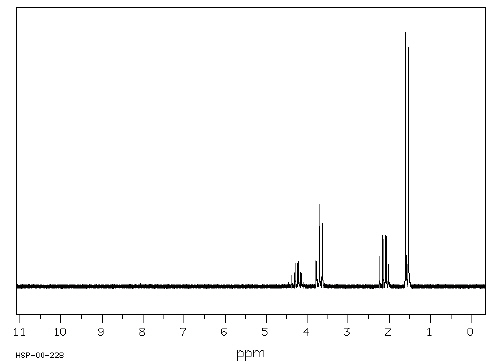 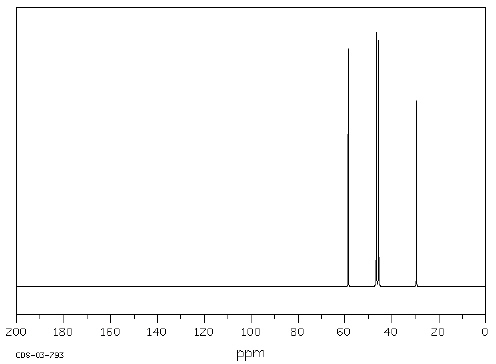 Spectra obtained from: SDBSWeb: http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS/
|
|
|
Exhibit 13-12
Answer the question(s) for the compound whose
1H NMR spectra is shown below. C 8H 7ClO 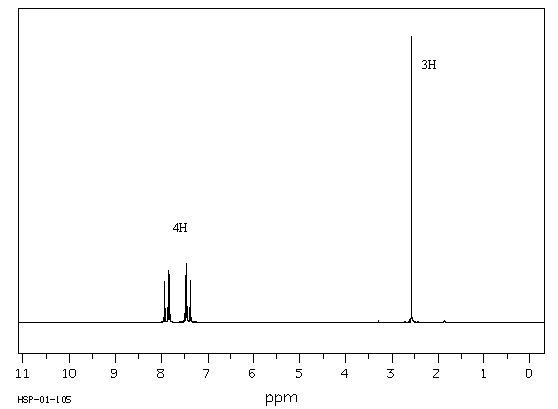 Spectrum obtained from: SDBSWeb: http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS/
|
|
|
84.
|
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. Calculate the degree of unsaturation in this
compound.
|
|
|
85.
|
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. Describe the signals that occur between 7 and 8 d in terms of integration, splitting and chemical shift.
|
|
|
86.
|
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. Describe the signal at 2.6 d
in terms of integration, splitting and chemical shift.
|
|
|
87.
|
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. Propose a structure for this compound.
|